5 robotics trends for 2026
The International Federation of Robotics reports on the five most important trends for the robotics industry in 2026
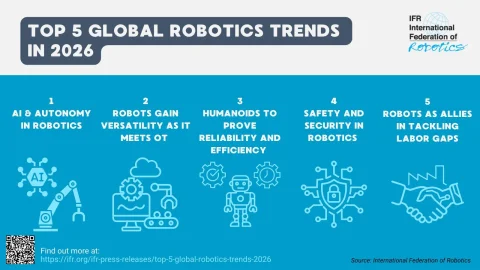
The global market value for industrial robot installations has reached a new high of USD 16.7 billion. Future demand will be driven by a range of technological innovations, market forces and new business areas. The International Federation of Robotics reports on the five key trends for the robotics industry in 2026.
1 - AI and autonomy in robotics
Robots that use artificial intelligence to work autonomously are becoming increasingly common. The main advantage of AI in this context is the increased autonomy of robots enabled by AI. Different types of AI are driving this trend: Analytical AI helps process large data sets, recognizes patterns and provides actionable insights. This enables them to independently predict failures before they occur in smart factories, for example, or to take over route planning and resource allocation in logistics.
Generative AI, on the other hand, marks a shift from rule-based automation to intelligent, self-developing systems. GenAI creates new results and enables robots to learn new tasks autonomously and generate training data through simulation. This also enables a new type of human-robot interaction with natural language and image-based commands.
An important trend in the further development of autonomy in robotics is agentic AI. This technology combines analytical AI for structured decision-making and generative AI for adaptability. The hybrid approach aims to enable modern robotics to work independently in complex, real-world environments.
2 - Robots become more versatile when IT meets OT
The demand for versatile robots is growing rapidly. This directly reflects the market trend towards a convergence of information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT). Merging the data processing power of IT with the physical control capabilities of OT enhances the versatility of robotics through real-time data exchange, automation and advanced analytics. This integration is a fundamental element of the digital enterprise and Industry 4.0. IT/OT convergence breaks down these silos and creates a seamless flow of data between the digital and physical worlds, greatly enhancing the capabilities and versatility of robotics.
3 - Humanoid robots must prove their reliability and efficiency
The field of humanoid robotics is growing rapidly. Humanoid robots for industrial use are considered a promising technology when flexibility is required, typically in environments designed for humans. Applications in warehousing and manufacturing have become established worldwide, particularly in the automotive industry.
Today, companies and researchers are moving beyond prototypes and using humanoids in real life. Reliability and efficiency are the key to success: in competition with traditional automation, humanoid robots must meet high industrial requirements in terms of cycle times, energy consumption and maintenance costs. Industry standards also define safety levels, durability criteria and the consistent performance of humanoid robots needed on the factory floor. Humanoids designed to fill labor gaps must achieve human-level dexterity and productivity to prove their efficiency in the field.
4 - Safety and security in robotics
As robots are increasingly used alongside humans in factories and service industries, ensuring their safe operation is not only important, but essential for the robotics industry. AI-driven autonomy is fundamentally changing the safety landscape, making testing, validation and human oversight much more complex, but also more necessary. This is particularly evident in the intended use of humanoid robots. Robotic systems must be designed and certified according to ISO safety standards and clearly defined liability frameworks.
In the context of AI in robotics and the convergence of IT and OT, a number of safety concerns arise that require robust governance and a clear allocation of liability. The rapid proliferation of robotic systems in cloud-connected and AI-driven environments is exposing industrial production to a growing number of cybersecurity threats. Experts point to an increase in hacking attempts targeting robot controllers and cloud platforms, allowing unauthorized access and potential system manipulation. As robots are increasingly integrated into workplaces, there are growing concerns about the sensitive data they collect - including video, audio and sensor streams. Deep learning models, often referred to as "black boxes", can produce results that are difficult or impossible to explain even to their own developers. The legal and ethical ambiguity regarding liability has led to calls for clear framework conditions for the use of AI.
5 - Robots as allies in tackling labor shortages
Employers around the world are struggling to find employees with the skills they need. These unfilled positions mean that existing employees have to take on additional shifts, leading to increasing stress and fatigue across all industries. An important strategy to solve this problem is the use of robotics and automation. In this transformation process, employers benefit from involving their human workforce. Working closely with employees when introducing robots plays a crucial role in their acceptance - both in industrial manufacturing and in the wide range of service applications. The benefits that robots offer, such as addressing labor shortages, taking over routine tasks or opening up new career opportunities, mean that they are accepted as allies in the workplace. At the same time, robots are a means of making the workplace more attractive to young people. Companies and governments are promoting upskilling and training programs to help workers keep pace with changing skill requirements and remain competitive in an automation-driven economy.