More efficient welding under water
The Laser Zentrum Hannover LZH is developing a laser-assisted metal flux-cored welding process for underwater use together with an industrial partner. The process aims to facilitate welding work and produce better weld seams.
Whether for wind farms, coastal protection structures, or harbors: when technical constructions have to be welded underwater, divers usually do it by manual electrode welding. Scientists of the LZH are now developing an alternative process together with AMT GmbH from Aachen. Laser-assisted metal flux-cored welding underwater aims to make welding underwater easier and produce better weld seams.
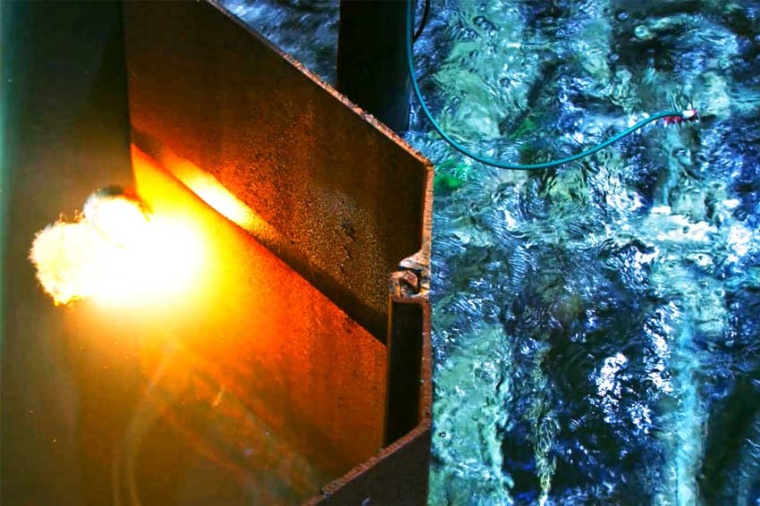
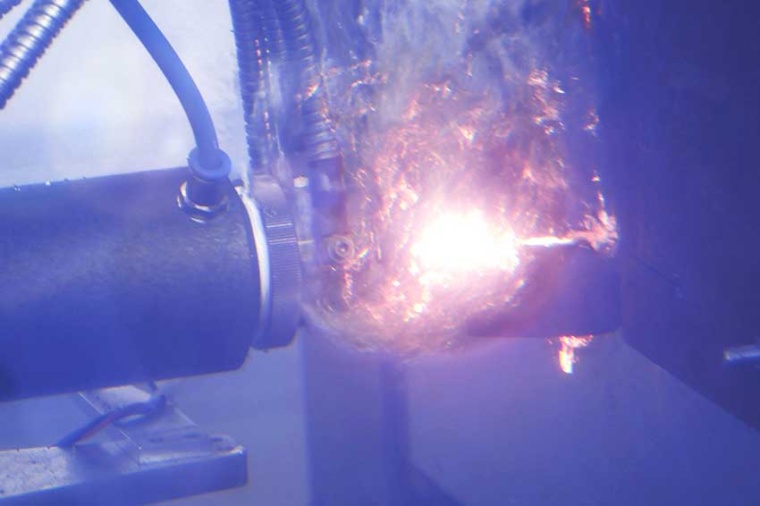


Manual electrode welding, which is relatively simple and inexpensive, has become established for underwater welding work. However, it has a major disadvantage: the diver must frequently replace the burnt electrodes. This means that the process has to be interrupted repeatedly, especially for longer welds.
In contrast, with flux-cored welding, the wire can be continuously taken from a wire reel, which is then melted. This allows significantly longer weld seams to be produced, thus increasing deposition rates and production rates. With the help of laser radiation, the LZH scientists now want to optimize flux-cored welding. The goal is to develop laser-assisted metal flux-cored welding as a qualitatively convincing and more efficient alternative for welding underwater.
Laser radiation shall improve arc ignition and process stability
The laser beam will insert energy into the workpiece in a targeted manner to improve arc ignition and stability. Research on laser beam-arc hybrid welding in an atmosphere has shown that the targeted combination of laser beam and arc in a common process zone allows the arc to be guided precisely, resulting in higher process stability and geometric accuracy of the weld seam. In addition, higher welding speeds and the over-welding of existing weld seams are possible. In the LaMeer project, the partners now want to research the combination of the laser beam and arc in underwater applications. To this end, they want to develop and test a welding torch prototype with integrated laser optics.
The increasing importance of underwater welding
The maritime industry is one of the most important sectors in Germany. Welding as one of the key technologies in underwater technology is becoming increasingly important, especially against the background of climate change, for example in the areas of energy generation and coastal protection. The LaMeer project (laser-assisted metal flux-cored welding underwater) is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Economics and Climate Protection under the funding code KK5111705SU1 by the project sponsor AIF Projekt GmbH.
Company
Laser Zentrum Hannover e.V.Hollerithallee 8
30419 Hannover
Germany
most read

Qioptiq Photonics becomes Excelitas Germany
The renaming is part of the global consolidation of the Excelitas Group.

Purdue University, Rittal and Eplan work together
As part of this partnership, Purdue will open two exclusive laboratories.

Physik Instrumente supports space research
The company is providing 2,500 hybrid actuators for the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT)

Lapp Group takes over JJ-Lapp completely
JJ-Lapp will now become a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Group, with financial details remaining confidential.

Machine Safety 2026: The Five Most Important Trends for Eutomation Engineers
Digitalization and automation continue to drive mechanical engineering forward - and with them, the requirements for functional safety and cyber security are increasing. For automation engineers, this means that machine safety is becoming a holistic concept.