Laser cleaning – underwater
The LZH, Laserline, and Fraunhofer IFAM, have developed a laser process to clean ship hulls.
Biofouling is the growth of algae, mussels, and other marine organisms on the hull of a ship. The fouling increases the flow resistance of the ship – and thus increases fuel consumption and CO2 emissions. Mechanical cleaning of the fouling can damage the hull coating. In addition, the fouling must be extracted if organisms or even parts of the ship's coating are not to get into the water. Scientists from the LZH, together with Laserline and the Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Applied Materials Research IFAM, have now developed an environmentally friendly and efficient solution to the problem of biofouling.
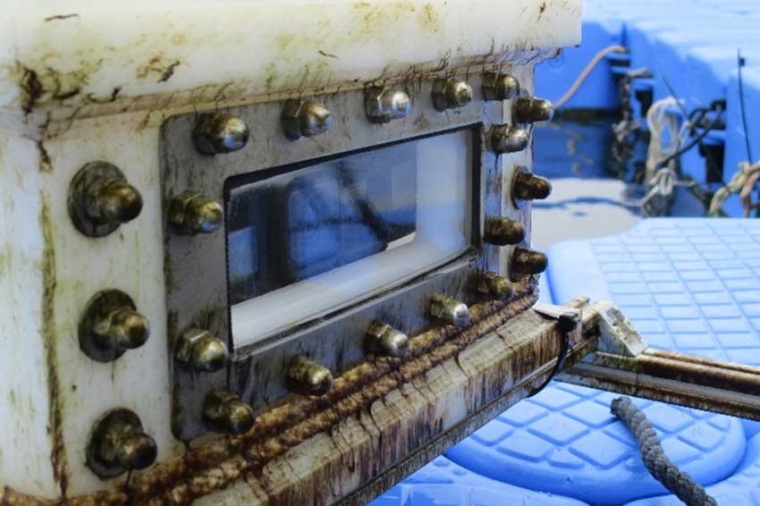
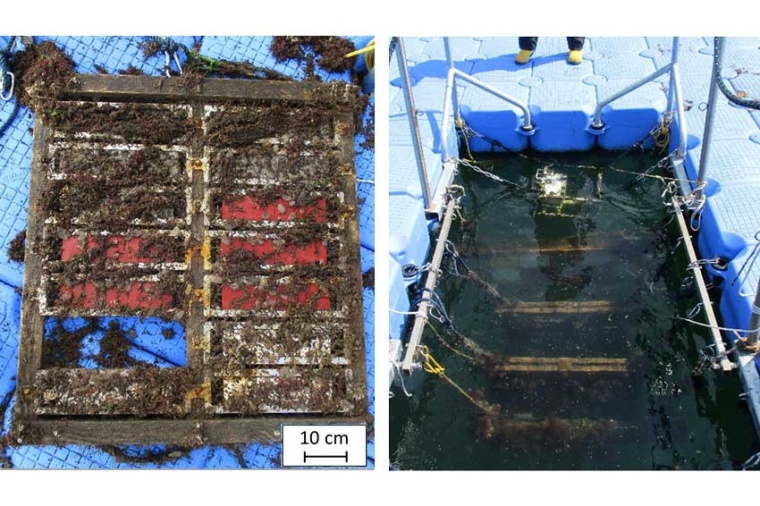


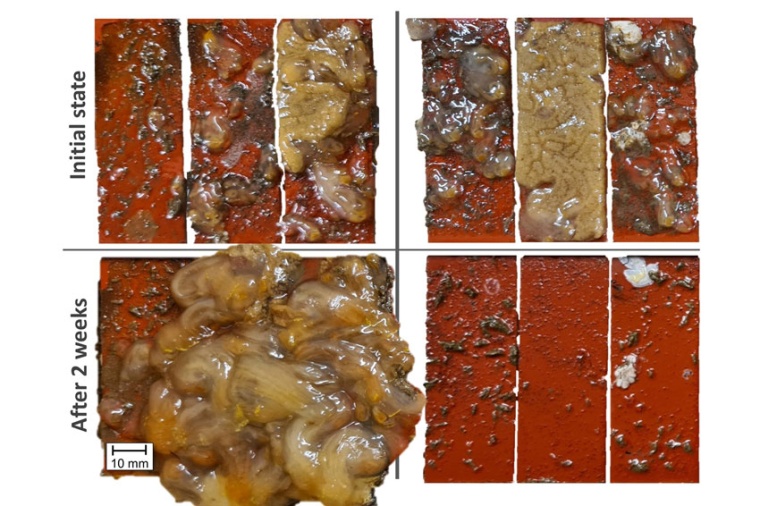
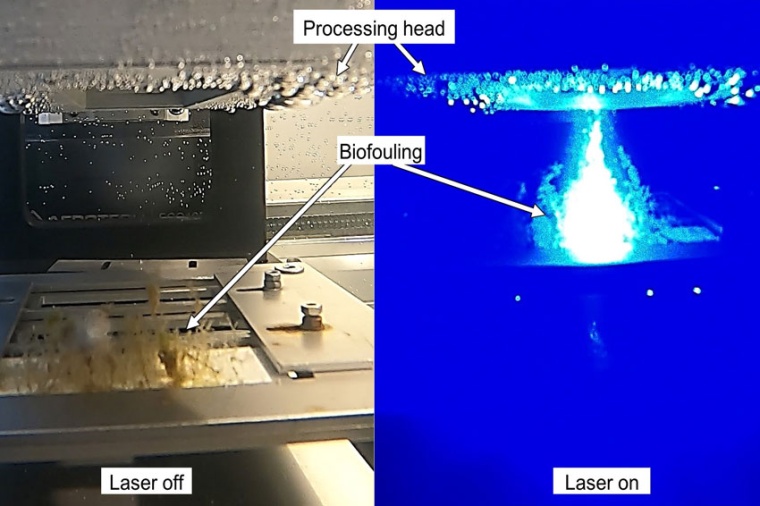
Laser radiation can be used to lethally damage marine fouling underwater without damaging the underlying coating of the ship’s hull. The LZH scientists have developed a process in which the cells of the fouling are damaged by laser radiation in such a way that the fouling dies and is then simply washed away by the water after some time.
The researchers conducted their investigations in the south harbor of the island of Helgoland. There, they irradiated fouling samples with the laser, then returned them to the North Sea and checked them after two to four weeks. “We were able to achieve a clear, time-delayed cleaning effect,” says underwater technology expert Dr-Ing Benjamin Emde from the LZH. “With simulated currents, as would be added in real life with a moving ship, the cleaning effect is further enhanced.”
And biofouling is not only a problem for reasons of fuel consumption and emissions: the fouling can lead to the introduction and spread of non-native species in foreign ecosystems. “Species displacement is a major risk of biofouling,” Emde says. If a ship introduces foreign organisms into an ecosystem through hull fouling, it can severely disrupt the ecosystem. In practice, this leads to ships being banned from docking in foreign ports, as has happened again recently with cruise ships, for example. Here, as well, cleaning with the laser is a good alternative to mechanical methods: Because the introduced biomass is lethally damaged during laser cleaning, it is no longer dangerous for foreign ecosystems.
Company
Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials IFAMWiener Straße 12
28359 Bremen
Germany
most read

Engineering labor market under pressure: shortage of skilled workers despite the crisis
Unemployment in IT and engineering professions rose by 17.6 percent, while the total number of vacancies fell by 23 percent to 99,470.

Agile Robots takes over Thyssenkrupp Automation Engineering
This acquisition is intended to strengthen Agile Robots' market position in the field of smart automation solutions

Ams Osram sells sensor business to Infineon
The sale includes companies with assets of around EUR 130 million, which will be used to repay convertible bonds and senior notes.
Siemens takes over Canopus AI
This expansion of the Siemens EDA software portfolio is designed to help chip manufacturers improve precision and efficiency in wafer and mask inspection processes.
Digikey significantly expanded its portfolio in 2025
The company has expanded its product portfolio by more than 108,000 new components and added 364 new suppliers.