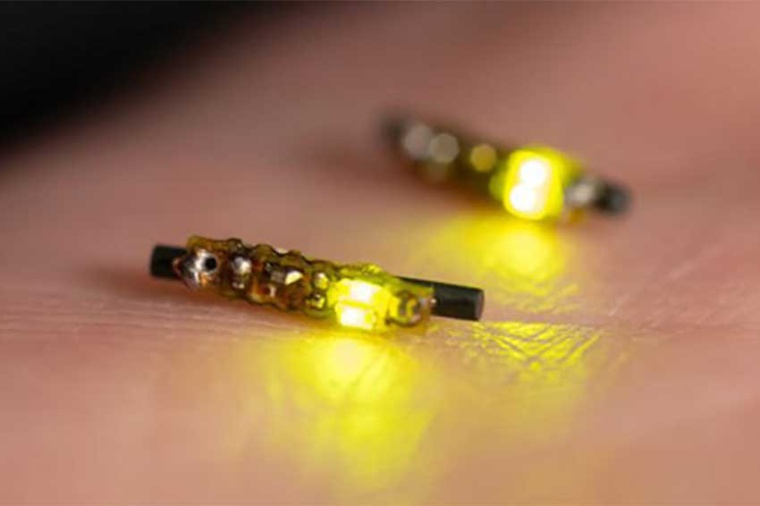
Implantable LED device to treat cancer
Photoactivated cells exhibited signs of cell death by light-induced pyroptosis.
Certain types of light have proven to be an effective, minimally invasive treatment for cancers located on or near the skin when combined with a light-activated drug. But deep-seated cancers, surrounded by tissue, blood and bone, have been beyond the reach of light’s therapeutic effects. To bring light’s benefits to these harder-to-access cancers, engineers and scientists at the University of Notre Dame have devised a wireless LED device that can be implanted. This device, when combined with a light-sensitive dye, not only destroys cancer cells, but also mobilizes the immune system’s cancer-targeting response.

“Certain colors of light penetrate tissue deeper than other ones,” said Thomas O’Sullivan. “It turns out that the kind of light – in this case green – that doesn’t penetrate as deeply has the capability of producing a more robust response against the cancer cells.” Before the light can be effective in destroying cancer cells, a dye with light-absorbing molecules must be administered to the cells. The device turns on, the dye transfers the light into energy and that energy makes the cells’ own oxygen toxic – in effect, turning the cancer cells against themselves.
While other treatments also weaponize the cells’ own oxygen, this device causes a particularly serendipitous form of cell death. “Working together, biochemistry graduate student Hailey Sanders and electrical engineering graduate student SungHoon Rho perceptively noted that the treated cells were swelling, which is the hallmark of a kind of cell death, pyroptosis, that’s particularly good at triggering the immune response,” said Bradley Smith. “Our goal is to induce just a little bit of pyroptotic cell death, which will then trigger the immune system to start attacking the cancer.”
In future studies, the device will be used in mice to see whether the cancer-killing response initiated in one tumor will prompt the immune system to identify and attack another cancerous tumor on its own. O’Sullivan noted that the device, which is the size of a grain of rice, can be injected directly into a cancerous tumor and activated remotely by an external antenna. The goal is to use the device not only to deliver treatment but also to monitor the tumor’s response, adjusting signal strength and timing as needed. (Source: U. Notre Dame)