ZwickRoell is testing moon dust as a building material for ESA project
Is a moon station from the 3D printer possible?
Should the construction of a base station on the moon begin in the near future, the testing machine manufacturer ZwickRoell could be involved. The company from Ulm-Einsingen tested samples of artificial moon dust for an Austrian company that cooperates with the European Space Agency (ESA). The question was: Is the material suitable for the future production of materials and tools for the construction of a lunar station using a 3D printer on the moon?
The moon as a "springboard to Mars" - and further into space: That is the vision behind the construction of a moon base - and for which international space agencies already have concrete plans. However, it is very expensive to transport building materials and tools from the earth to the moon. That is why Lithoz GmbH from Vienna, a specialist in technical ceramics in 3D printing, developed a new process for the European Space Agency (ESA). This can be used to produce building materials, spare parts and tools from synthetic moon dust using a 3D printer with LCM technology.
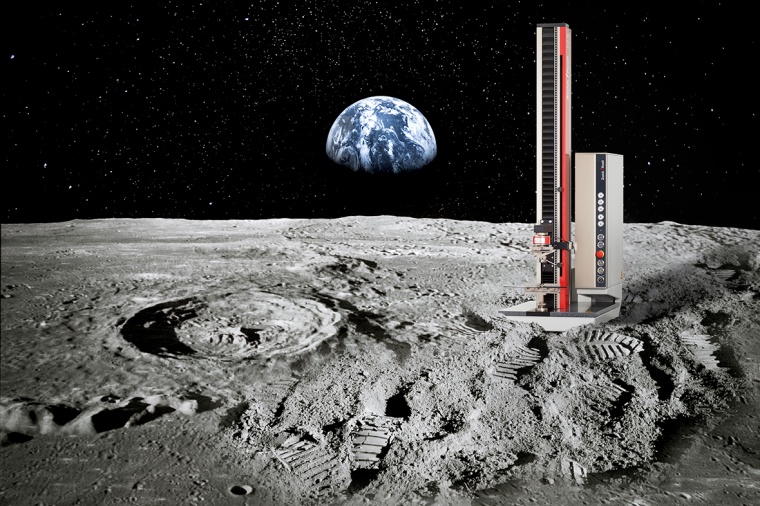
ZwickRoell test engineers examined the regolith samples, which is artificially produced moon dust. These samples, manufactured using the sintering process at +1100° C and +1200 °C, were subjected to pressure and 3-point bending tests in order to determine their special properties in terms of resilience. But why were samples of synthetic, i.e. "artificial" produced on Earth, moon dust used for the tests? Homa reports that there are very simple reasons for this: “There are around 400 kilograms of moon dust on Earth from earlier moon missions. But this is now contaminated by the air and moisture. In addition, it has lost its chemical reactivity and is therefore unusable for today's experimental purposes." However, the artificially produced regolith has "almost 100 percent identical chemical, mechanical or technical properties and characteristics to real moon dust."
Test results are analyzed and discussed with ESA
The tests in the ZwickRoell laboratory at the Ulm-Einsingen site lasted two days. "For us, the material tests with Regolith represented a novelty, which we were able to carry out very well according to the special customer requirements," summarizes Tobias Ebner, the materials engineer responsible for the sample tests of the "Moon Dust" project. And he adds: "The evaluation of the test results, whether and to what extent the material is suitable for the construction of a lunar station or whether it sometimes needs to be adapted, is now the responsibility of our client." The results and findings of the two-day quality tests are currently being analyzed by Lithoz GmbH , discussed with ESA and subsequently published.
Company founders learned on ZwickRoell testing machines
But how did the cooperation between ZwickRoell and the Viennese company come about? The connection "Vienna - Ulm" has existed since the student days of the two managing directors Johannes Benedikt and Johannes Homa. Homa: “We were already working with ZwickRoell machines when we were studying materials science. As a very reliable and quality-conscious partner, ZwickRoell smoothed our way from start-up to world market leader, so to speak. That is why the Ulm-based company is now accompanying us on this special lunar mission.” When the construction of a lunar station will actually begin is currently still in the stars. But one thing is "already fixed". Homa: “Anyone who flies to the moon cannot get past us. We want to – in the truest sense of the word – reach for the stars and make the conceivable possible and implement it in space with our competence. Or spoken in Latin: Per aspera ad astra ("To the stars through difficulties"). Thanks to ZwickRoell, we have taken a big step forward.”