Intelligent optical chip to improve telecommunications
An INRS team uses autonomous learning approaches for optical waveform generators to boost optical signal processing functionalities for current and future telecom applications.
From the internet, to fiber or satellite communications and medical diagnostics, our everyday life relies on optical technologies. These technologies use optical pulsed sources to transfer, retrieve or compute information. Gaining control over optical pulse shapes thus paves the way for further advances.
PhD student Bennet Fischer and postdoctoral researcher Mario Chemnitz, in the team of Professor Roberto Morandotti of the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS), developed a smart pulse shaper integrated on a chip. The device output can autonomously adjust to a user-defined target waveform with strikingly low technical and computational requirements.
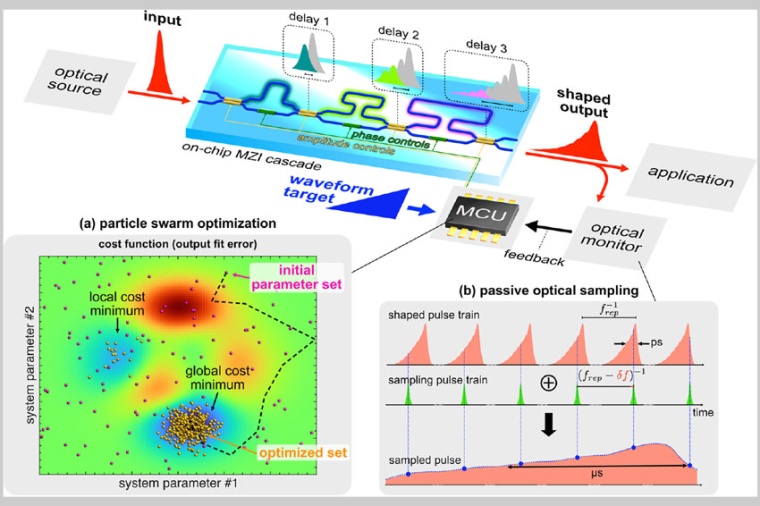

Ideally, an optical waveform generator should autonomously output a target waveform for user-friendliness, minimize the experimental requirements for driving the system and reading out the waveform, to ease online monitoring. It should also feature a long-term reliability, low losses, fiber connectivity, and maximal functionality.
“Previously demonstrated integrated optical waveform generators only featured one or two of these key features at a time. Our methods address all the demands in one scalable, potentially fully chip integrable approach,” Chemnitz explains.
Among other things, practical imperfections, such as individual device fidelities, deteriorate the performances accessible from those initially designed or simulated for. “We find that evolutionary optimization can help in overcoming the inherent design limitations of on-chip systems and hence elevate their performance and reconfigurability to a new level,” says the postdoctoral researcher.
The team was able to achieve this device alongside with the recent emergence of machine learning concepts into photonics, which promises unprecedented capabilities and system performance. “The optics community is eager to learn about new methods and smart device implementations. In our work, we present an interlinked bundle of machine-learning enabling methods of high relevance, for both the technical and academic optical communities.”
The researchers used evolutionary optimization algorithms as a key tool for repurposing a programmable photonic chip beyond its original use. Evolutionary algorithms are nature-inspired computer programs, which allows to efficiently optimize many-parameter systems at significantly reduced computational resources.
The team’s next steps include the investigation of more complex chip designs. The target is to improve the device performance, as well as the on-chip integration of the optical sampling (detection scheme). At terms, they could provide a single compact device ready-to-use. (Source: INRS)
Reference: B. Fischer et al.: Autonomous on-chip interferometry for reconfigurable optical waveform generation”, Optica 8(10); DOI: 10.1364/optica.435435
most read
Siemens takes over Canopus AI
This expansion of the Siemens EDA software portfolio is designed to help chip manufacturers improve precision and efficiency in wafer and mask inspection processes.

Helukabel joins the IPAI
This platform promotes the development and application of artificial intelligence (AI) through collaboration between companies, research facilities and institutions.

Engineering labor market under pressure: shortage of skilled workers despite the crisis
Unemployment in IT and engineering professions rose by 17.6 percent, while the total number of vacancies fell by 23 percent to 99,470.

Agile Robots takes over Thyssenkrupp Automation Engineering
This acquisition is intended to strengthen Agile Robots' market position in the field of smart automation solutions

Ams Osram sells sensor business to Infineon
The sale includes companies with assets of around EUR 130 million, which will be used to repay convertible bonds and senior notes.